Construction sites are dynamic environments where worker safety and operational efficiency are paramount. There are various technologies and strategies available to enhance safety, improve workflow, and streamline asset management. Below, we compare several common solutions—both with and without wearables—to highlight their advantages and show how smart wearables provide additional benefits.
1. Worker Safety Solutions
a. Traditional Proximity Sensors (Non-Wearable)
Technology: Infrared, capacitive, ultrasonic, and radar sensors.
Use Case: Detecting workers’ presence in hazardous areas (e.g., near heavy machinery, construction zones).
How It Works: Proximity sensors are mounted on equipment, gates, or areas to detect nearby workers. When workers enter a dangerous zone, the sensors trigger alerts or stop equipment.
Advantages:
- Simple to install and use.
- Can automatically stop machinery to prevent accidents.
- Cost-effective for basic safety monitoring.
Limitations:
- Limited to specific zones; workers not wearing proximity badges may not be detected.
- Only provides static alerts; does not track workers’ real-time location.
- Limited scalability for large, dynamic construction sites.
b. Smart Wearables (e.g., Smartwatches)
Technology: Bluetooth, GPS, accelerometers, and health monitoring sensors.
Use Case: Continuous monitoring of worker health and location, proximity alerts to hazardous zones, fall detection, emergency SOS.
How It Works: Workers wear smartwatches with built-in sensors to detect vital health metrics (heart rate, blood oxygen), movement (fall detection), and location. These wearables can trigger alerts if workers are too close to hazardous zones or if health conditions exceed predefined thresholds.
Advantages:
- Real-time monitoring: Tracks workers’ location and health metrics in real time.
- Personalized alerts: Provides immediate feedback to workers through vibration or notifications.
- Emergency response: Immediate SOS alerts can be sent if a worker is in danger, or if a fall is detected.
- Scalability: Easy to implement across large teams without additional infrastructure.
- Data analytics: Health and safety data can be used to improve site operations and worker well-being.
Limitations:
- Initial investment in wearables for all workers.
- Requires ongoing maintenance and updates for firmware.
Comparison Summary:
- Traditional Proximity Sensors are a great way to monitor fixed safety zones and trigger alerts, but they are limited by static zone detection and lack of real-time tracking.
- Smart Wearables go beyond static zone safety, offering dynamic, real-time monitoring of worker location, health, and alerts. This allows for quicker responses to safety issues and personalized feedback for workers.
iSmarch Wearables: Advanced Worker Safety
iSmarch wearables take safety to the next level by combining health monitoring, real-time location tracking, and environmental hazard detection into a single device. Our LoRaWAN-enabled smart wearables provide continuous heart rate, SpO2, HRV, and respiration monitoring, ensuring that workers’ health is actively tracked. This data is sent in real-time to backend systems, alerting supervisors if a worker is at risk of fatigue, heat stress, or other health issues.
Our wearables also come equipped with location tracking technologies, such as GPS for outdoor tracking and Bluetooth beacons, AoA(cuztomized option), or UWB(cuztomized option) for indoor positioning. This means that workers’ movements are constantly monitored, and emergency alerts can be triggered if a worker enters a hazardous zone or experiences a fall. The integration of LoRaWAN technology ensures long-range communication, making it ideal for large construction sites.
By using iSmarch smart wearables, managers can get a holistic view of worker health and safety, respond to incidents in real-time, and ensure compliance with safety regulations—ultimately improving overall site safety.
That’s a great idea! Creating a comparison content that highlights the advantages of implementing smart wearables while also outlining other typical safety and management solutions can help emphasize the unique benefits wearables bring to construction sites. Below is a draft content structure that you can build upon, which compares different solutions for worker safety, workflow efficiency, and equipment management, emphasizing where smart wearables stand out.
2. Workflow Efficiency
a. GPS/Geofencing (Non-Wearable)
Technology: GPS-based tracking and geofencing.
Use Case: Tracking worker or asset movement, ensuring they are in designated work zones, optimizing workflows.
How It Works: GPS trackers are installed on vehicles, equipment, or workers to monitor movement. Geofencing creates virtual boundaries, triggering alerts when workers or assets leave or enter a specific area.
Advantages:
- Accurate, real-time location tracking.
- Can improve site efficiency by ensuring workers are within the right work zones.
Limitations:
- May require additional infrastructure (e.g., base stations or receivers).
- Tracking devices can be lost, damaged, or require battery replacements.
- Less effective in confined or indoor areas with GPS interference.
b. Smart Wearables with GPS and Beacon Integration
Technology: GPS, Bluetooth (beacons), and LoRaWAN (for long-range communication).
Use Case: Providing real-time worker tracking, ensuring workers are within designated areas, improving task assignment and site management.
How It Works: Smartwatches can be equipped with GPS for outdoor tracking and Bluetooth for indoor positioning (via beacons). Workers’ real-time locations are continuously updated and can be monitored via a central dashboard.
Advantages:
- Seamless integration: Works both indoors (via Bluetooth beacons) and outdoors (via GPS).
- Advanced location tracking: Provides precise location data for workflow optimization.
- Dynamic task management: Allows supervisors to assign tasks based on workers’ current location, improving task flow and efficiency.
Limitations:
- Requires the integration of beacons or infrastructure for indoor tracking.
- Battery life needs to be optimized for continuous use.
Comparison Summary:
- GPS and Geofencing are essential for tracking large areas and managing worker movement, but they may struggle in indoor or highly confined spaces.
- Smart Wearables offer more flexibility and precision with the ability to combine GPS and indoor beacon positioning, providing real-time worker tracking for better workflow management and site optimization.
iSmarch Wearables: Enhancing Workflow Efficiency
iSmarch wearables enhance workflow efficiency by integrating location tracking, task management, and real-time data sharing in a single wearable device. Our wearables use high-accuracy GPS for outdoor navigation and work seamlessly with Bluetooth beacons and other positioning systems for indoor environments, enabling precise worker and asset tracking throughout the construction site.
With iSmarch smart wearables, workers and supervisors benefit from automated workflow management and real-time communication, reducing manual efforts, improving task completion rates, and increasing overall productivity.
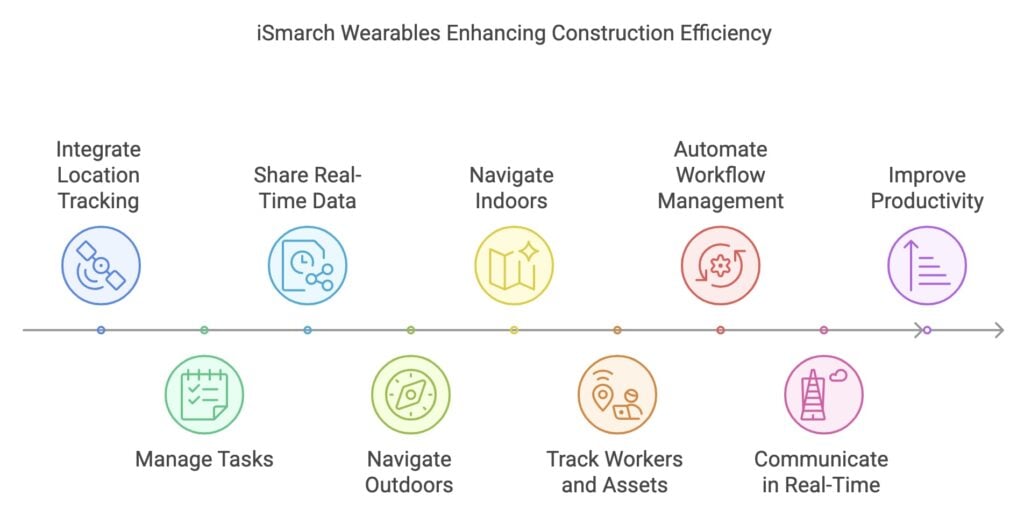
3. Equipment Management and Asset Tracking
a. RFID Tags (Non-Wearable)
Technology: Radio Frequency Identification (RFID).
Use Case: Tracking equipment, tools, and materials across a construction site.
How It Works: RFID tags are attached to tools or equipment. When the item passes through an RFID reader, its location is recorded, allowing managers to track its movement.
Advantages:
- Simple and low-cost solution for asset tracking.
- Helps prevent theft and loss.
Limitations:
- Limited range compared to GPS-based systems.
- Requires manual scanning or specific RFID readers.
- Does not provide real-time alerts for immediate issues.
b. Smart Wearables with Beacon Technology for Asset Tracking
Technology: BLE, RFID, and GPS.
Use Case: Real-time tracking of both workers and assets.
How It Works: Smartwatches can communicate with equipment and tool beacons using Bluetooth, automatically recording equipment usage or asset locations. They can also alert supervisors if equipment is moved outside designated zones.
Advantages:
- Real-time monitoring: Tracks both workers and equipment simultaneously in real time.
- Integration with workers’ movements: Ensures assets are being used by the right personnel and in the correct locations.
- Advanced alerts: Immediate notifications when equipment is moved or misused.
Limitations:
- Requires initial setup and integration of beacons and wearable devices.
Comparison Summary:
- RFID is cost-effective for simple asset tracking but lacks the real-time, dynamic interaction that wearables can provide.
- Smart Wearables integrated with beacon technology offer advanced features like real-time alerts and worker-equipment interactions, ensuring more precise and automated asset management.
iSmarch Wearables: Integrated Asset and Equipment Management
iSmarch wearables provide a comprehensive solution for asset management by integrating worker tracking with equipment usage monitoring. Our wearables can be equipped with RFID or Bluetooth beacon capabilities to track assets and tools in real-time. Supervisors can monitor asset movements across the site, ensuring that tools and machinery are being used appropriately.

4. Environmental Hazard Monitoring
Typical Goals:
- Monitor Exposure to Dangerous Environments: Detect hazardous gases, extreme temperatures, or other unsafe environmental factors.
- Prevent Heat Stress & Dehydration: Ensure workers are not exposed to excessive heat or conditions that may lead to exhaustion.
Environmental Sensors (Non-Wearables)
How it Works: Environmental sensors monitor the presence of hazardous materials (e.g., gas detectors) or extreme conditions (e.g., heat, humidity) in the environment.
Advantages: Non-invasive, low-maintenance, and accurate in detecting hazardous environments.
Limitations: Does not provide real-time health or location data for workers themselves.
Smart Wearables with Environmental Sensors
How it Works: Smartwatches can be equipped with temperature sensors, humidity detectors, and gas sensors to monitor the environment surrounding workers. Additionally, they can track the workers’ health metrics, such as heart rate and body temperature, to identify when workers are at risk of heat stress or exhaustion.
Advantages: Real-time environmental and health monitoring in one device, early alerts for both workers and supervisors if hazardous conditions are detected.
Limitations: Need for continuous monitoring of wearables and reliable data integration.
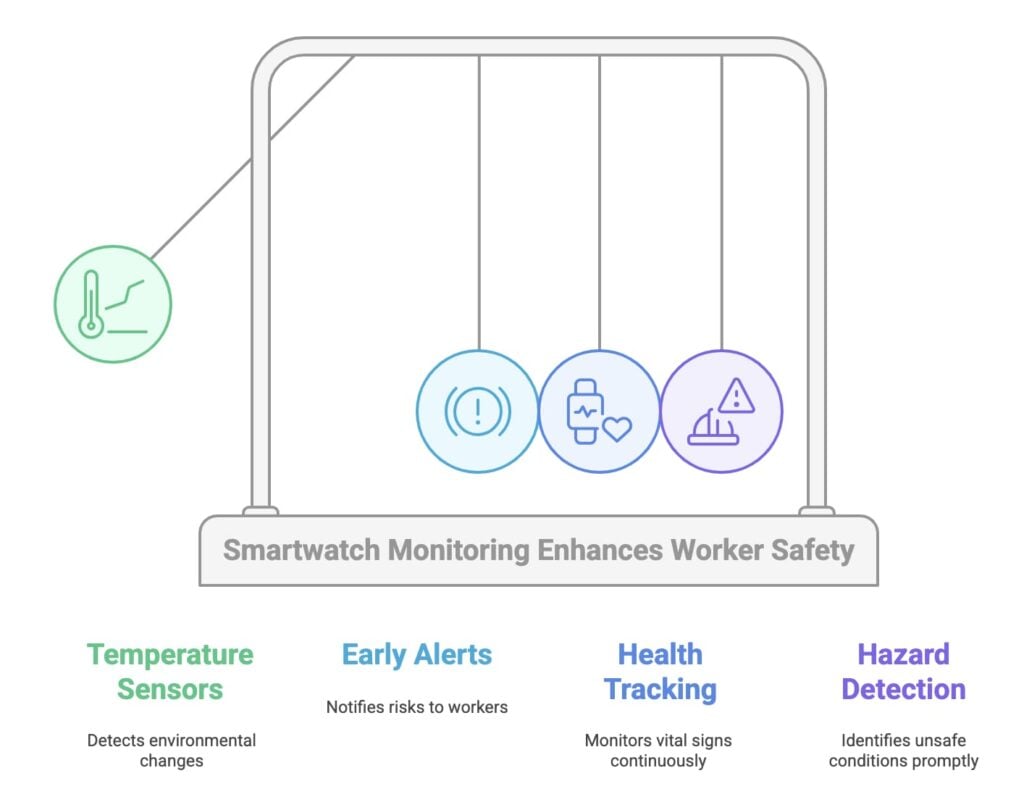
Comparison:
- Environmental sensors can detect hazardous conditions, but they do not track the well-being of workers.
- Smart wearables provide a holistic solution by monitoring both the environment and the worker’s physical condition, giving workers more protection from environmental hazards.
5. Communication and Coordination
Typical Goals:
- Improve Team Communication: Ensure that workers can quickly communicate with each other and supervisors, especially in emergency situations.
- Real-time Updates: Provide workers and supervisors with real-time updates on project changes, tasks, and safety protocols.
Two-Way Radios (Non-Wearables)
- How it Works: Two-way radios allow workers and supervisors to communicate over long distances on the site.
- Advantages: Reliable, simple to use for large teams in areas without cellular coverage.
- Limitations: Limited to verbal communication, no integration with location, health, or task management.
Smart Wearables with Communication Features (e.g., Smartwatches with Push-to-Talk)
- How it Works: Smartwatches equipped with push-to-talk (PTT) functionality enable workers to instantly communicate with supervisors and colleagues. They can also receive real-time notifications about site changes or safety alerts.
- Advantages: Instant communication integrated with location and health data, enabling supervisors to make informed decisions quickly.
- Limitations: Requires workers to wear the device and ensure battery management.
Comparison:
- Two-way radios are effective for communication but do not offer integration with location, health monitoring, or task management.
- Smart wearables combine communication with real-time health, location tracking, and emergency alerts, providing a more integrated communication system.
iSmarch Wearables: Enhanced Communication and Coordination
iSmarch wearables like smart helmet can provide pre-recorded voice alert throught its built in speaker, iSmarch wearables integrate real-time health monitoring, location tracking, and task management, enabling seamless coordination and quick response in emergencies.
6. Customization Flexibility: iSmarch’s Advantage
One of the key differentiators of iSmarch wearables is our customization flexibility. Construction sites often have specific requirements, whether it’s monitoring gas exposure, worker fatigue, or precise indoor positioning. iSmarch offers the ability to customize hardware (e.g., adding gas detectors, Wi-Fi modules, or other sensors) and firmware to meet the unique needs of each project.
This level of flexibility makes iSmarch wearables ideal for large-scale construction operations that need to integrate with existing systems or develop entirely new solutions.
Comparison Chart
| Category | Traditional Solutions | iSmarch Wearables |
|---|---|---|
| Worker Safety | – Proximity sensors for zone detection – Basic health monitoring (e.g., PPE) – Limited real-time alerts | – Real-time health monitoring (Heart Rate, SpO2, HRV, Respiration) – GPS & Bluetooth-based indoor/outdoor positioning – Real-time emergency alerts (e.g., falls, fatigue, health risks) – Integration with safety management systems |
| Workflow Efficiency | – Manual task assignment – Limited indoor location tracking – Basic project management tools | – Indoor and outdoor positioning (GPS, Bluetooth, AoA, UWB) – Real-time worker location and task progress monitoring – Optimized worker allocation and dynamic scheduling |
| Equipment Management | – RFID tags for asset tracking – Manual logs for maintenance – Basic GPS tracking for equipment | – IoT-enabled asset tracking via Bluetooth or RFID – Real-time equipment usage and location tracking – Integration with maintenance management systems |
| Communication & Coordination | – Two-way radios – Manual alerts and notifications – Limited integration with other systems | – Integrated real-time data sharing (health metrics, location, tasks) – Seamless integration with site management systems – Proactive coordination based on real-time data |
| Customization & Flexibility | – Basic adjustments to sensors (e.g., environmental) – Limited integration with existing systems | – Full hardware and firmware customization (add sensors like gas detectors, Wi-Fi, etc.) – SDKs for platform integration and data customization – Tailored solutions for specific site needs |
| Energy Efficiency | – Limited energy optimization, devices may require frequent charging | – Ultra-low power consumption with NRF52840 chipset – Long battery life and over-the-air (OTA) updates – Ideal for continuous, long-term use on construction sites |
Take the Next Step Towards a Smarter, Safer Construction Site
Are you ready to enhance worker safety, boost workflow efficiency, and streamline equipment management on your construction site? iSmarch wearables provide the cutting-edge technology and flexibility needed to transform your operations.
Contact us today to learn more about how our LoRaWAN-enabled smart wearables can integrate seamlessly into your construction site. Whether you’re looking to customize your devices for specific needs, improve safety standards, or optimize workflows, iSmarch is here to provide the most reliable, innovative, and adaptable solutions.
Get in touch with our team for a personalized consultation, demo, or to request more information about our products and services.



